Top 25 Cybersecurity Interview Questions
With the emerging trend of the Internet there the emergence of threats to network security.
Therefore there is the sudden rise in cyber security experts jobs in the globe.
If you are fresher and preparing for an interview, then the interviewer will try to see your cybersecurity knowledge also. So here are the list of Question that can asked related to cybersecurity.
Top 25 Cybersecurity Interview Questions
1. What is Cybersecurity or data security?
Cybersecurity or Data security requires the protection of information and property from fraud, corruption, or natural disaster, while allowing the information and property to remain available and beneficial to its intended users.
The term computer system protection refers to the set of processes that protect sensitive and valuable information and services of an individual and an organization.
2. Describe the basic component of computer security. Or describe CIA Traids?
The computer security is based on the confidentially, integrity and availability. These are the basic component of computer security.
- Confidentially: The purpose of this is to ensure that only those individuals who have the authority to view a piece of information may do so. No unauthorized individual should ever be able to view data, they are not eligible.
- Integrity: it is a related concept but deals with the generation and modification of data. Only authorized individuals should ever be able to create or change information.
- Availability: The goal of availability is to ensure that the data or the system itself, is available for use when the authorized user wants it.
Two additional security goals have been added to the original three in the CIA of security:
- Non-Repudiation : which deals with the ability to verify that a message has been sent and received and that the sender can be identified and verified. The requirement for this capability in online transaction should also be readily apparent.
- Authentication : it deals with the desire to ensure that an individuals is who they claim to be. The need for this in an online transaction is obvious.
3. Define the following Terms:
Attack: Attack are the attempts by unauthorized individuals to access or modify information of the system.
Vulnerability: A Vulnerability can be defined as a weakness in the system. Means your system is vulnerable or exposed to threat.
Threat: A threat to a system is a set of factors that has the potential to cause loss or harm. For example, malware is a threat to security they can steal your personal details and can make your system vulnerable for attack.
4. Explain the Term Virus and Worms?
A virus is a program or software that is loaded onto your computer without your knowledge and performs activities or tasks aganist your wish.
Virus can also replicate themselves. All computer viruses are man-made.
Even such a simple virus is dangerous because it will quickly use all available memory and bring the system halt.
A dangerous type of virus is capable of transmitting itself across network and breaching a security system.
Worms is a special type of virus that can replicate itself and use memory, but cannot attach itself to other programs.
They are malicious program that spread themselves automatically.
It can spread by exploiting vulnerabilities in the computer system, then using network connection find and attack other vulnerable systems.
The lack of human intervention allows worms to spread much faster than virus.
5. Explain the threats to security in details?
- Virus and worms: Virus is a program or piece of code that is loaded into your computer without your knowledge and they can replicate themselves. Worms is a special type of virus that can replicate itself and use memory, but cannot attach itself to other programs.
- Intruders: Intruders are those who are accessing computer systems and networks without authorization. Intruders are extremely patient since the process to gain access to the system takes persistence and dogged determination. If the first attack may fail, then intruders will try in another angle. They will search for another possible vulnerability that may not have been patched.
- Trojan: It is perhaps the most complex of all risks. Most of the common threats to banking come from the trojan family including Zeus and SpyEye. This has the power to hide from the detection of antivirus, and to steal valuable banking data to damage your bank account.
- Spyware: Spyware is a malware intended to spy on the computer of the victim. If you are infected with it.The spyware possibly will spy on your regular life or other life and it will find itself a way to contact this malware’s host.
6. Explain backdoor?
Backdoor: It not really malware, but it is a type of method where attackers will be able to bypass all of the standard authentication service if a device becomes vulnerable to this process.
7. Explain in brief what is D Dos Attack?
DDoS- It is the most famous type of attack, in which an attacker directs millions of traffic to the host system.
Because of this host system can’t handle this amount of traffic and crashes, taking advantage of this situation attacker steals the information.
8. Enlist Types of Attacks?
There are two types of attacks, namely active and passive attacks.
9. Explain Active Attacks?
The attacker attempts to bypass or hack into locked networks during an aggressive attack. attackers do this by deception, malware, worms, or trojan horses.
Active attacks include attempts to bypass or crack security software, installing malicious code and stealing or altering information.
10. Explain Passive Attacks?
A passive attack attackers passively analyze the vulnerability in system and if they find so
Passive attacks include traffic analysis, unprotected communications monitoring, weakly encrypted traffic decryption, and the capture of authentication information such as passwords.
11. Describe the phases of Virus?
Dormant Phase This virus is an idle one and activated by some event such as a file operations.
Propagation Phase: Virus places an identical copy of itself and try to propagate itself.
Triggering Phase : Virus gets activate to perform some functions
Execution Phase : Virus is running.
12. Difference Between Insiders and Intruders?
| Insiders | Intruders |
|---|---|
| Insiders are the authorized users, who try to access system or netwrok for which they not authorized. | Intruders are unauthorized individual who try to access internal and confidential system. |
| Insiders are the individual or group of individuals, from the same organization. | Intruders are the individual or group of individuals, having the intent to steal valuable information. |
| Have access and knowledge to cause immediate damage to the organisation. | They have to gain knowledge first because they are the outsiders, know nothing about an organization. |
| Insiders are more dangerous than Intruders. | Intruders are less dangerous, as they know nothing about private information. |
| It be any person from respective company like- manager, CEO etc | Intruders are generally hackers. |
13. Describe Piggy packing and Shoulder surfing?
Piggybacking is the event in which attacker closely follows behind a person who has just used their own access card or PIN to gain physical access to a room or building.
Suppose you access ATM machine, an attacker can trace your finger print and can easily understand your pin number.
Shoulder surfing is a similar process like Piggybacking. In this attackers set their position in such away that they are able to observe the authorized user entering the correct access code.
Suppose you enter your password for the Gmail account and someone follows it and learns your password, Now he/she will have access to your Gmail account.
14. What do you mean by dumpster driving, Explain it in detail?
Dumpster diving usually means looking for something valuable by way of trash or garbage.
Often this is done to uncover useful information that can help an individual gain access to a network.
Most of the time people have a habit of writing ID and password in a paper, and sometimes they throw it in dustbin without scratching the page.
Because of which an Attacker can easily hack your personal data. When dumpster diving, hackers look for:
Phone lists
An attacker can easily understand the power structure of the company, Learns possible account names. Suppose in the phone list if the attacker gets information(access ID) about security manager so an attacker can easily breach the security of the organization.
Memos
Reveal activities inside the target organization.
Policy manuals
Today’s employee manuals give instructions on how not to be victimized by hackers, and likewise, help the hacker know which attacks to avoid.
Calendars of events
It tells the hackers At which date and time every employee of the organization will be elsewhere and not logged into the system. In simple terms, he/she will information on the best time to break-into the security system.
System manuals, packing crates
It gives information to hackers about new systems or organization that they can break into.
Print outs
Source code is frequently found in dumpsters, along with e-mails (revealing account names), and Post; notes containing written passwords.
Disks, tapes, CD-ROMs
People forget to erase storage media, whic results in the exposure of sensitive data. These days, dumpsters may contain a larger number of “broken” CD-Rs. The CD-ROM “burning” process is sensitive, and can lead to failures, which are simply thrown away.
However, some hackers can still read these half destroyed disks, allowing the hacker to read a half-way completed backup or an other sensitive piece of information.
15. How can you prevent dumpster diving?
Destroy all sensitive information including junk mail and paperwork that includes:
- Account numbers
- Addresses
- Birth dates
- E-mail addresses
- Names
- Passwords and PINs
- Phone numbers
- Signatures
- Social Security Numbers
16. Define the Terms Cryptography, Cryptanyalsis, and Cryptology?
Cryptography:
Cryptography is an ancient art and science of writing in the secret message. Encoding simple messages in a secret form is defined as Cryptography.
Cryptanalysis:
The process of breaking any cipher text message to obtain the original message itself is known as cryptanalysis.
Cryptology:
It is a combination of cryptography and cryptanalysis.
In cryptography, a cipher is an algorithm used for performing encryption and decryption.
17. What is Encryption?
In technical term process of converting simple plain text into cipher text is know as encryption.
18. Describe caesar’s cipher encryption algorithm?
- It is a very simple and well-known encryption technique. Here, we re[lace plaintext by a letter with some fixed number of positions from the alphabets
- For example, a shift in this cipher we shift 3 positions, we replace A is by D and B by E and so on
- This method is invented by Julius Caesar, who use it to communicate with his generals hence the name Caesar‟s Cipher.
- We can represent the transformation by arranging the position of two alphabets.
- Examples :
Plain text: ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
Cipher text: DEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABC
To encrypt a message, simply look up each letter of the message in the “plain” line and write down the corresponding letter in the “cipher” line. To decipher, do the reverse.
Plain text: “the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog”
Cipher text: WKH TXLFN EURZQ IRA MXPSV RYHU WKH ODCB GRJ
The encryption can also be represented using modular arithmetic by first transforming the letters into numbers, according to the scheme, A = 0, B = 1, …, Z = 25. Encryption of a letter x by a shift n can be described mathematically as,
En (x) = (x + n) mod 26 Decryption is performed similarly, Dn (x) = (x – n) mod 26
Modified version of Caesar cipher:
In this version, alphabet A is replace by any other alphabet in the English alphabet set i.e. A to Z. so for each alphabet in the string we have 25 possibilities of replacement.
An attack on a cipher text message, wherein the attacker attempts to use all possible permutations and combinations as a Brute-force attack.
19. Explain rail fence cipher?
- The Rail Fence Cipher is a type of transposition cipher. The name is given from the way in which it is encoded.
- In the rail fence cipher, the plaintext message is written downwards on successive “rails” of fence, starting a new column when the bottom is reached. Then, the message is read according to the rows.
- For example, if we have two “rails” and a message is “WELCOME STUDENTS‟ then the message would be: The Rail Fence Cipher is a type of transposition cipher. The name is given from the way in which it is encoded.
- In the rail fence cipher, the plaintext message is written downwards on successive “rails” of fence, starting a new column when the bottom is reached. Then, the message is read according to the rows.
- For example, if we have two “rails” and a message is “WELCOME STUDENTS‟ then the message would be :
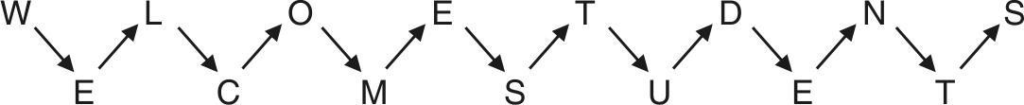
Then reads off : WLOETDNSECMSUET
Example – “COMPUTER SECURITY”

Output – “CMUESCRTOPTREUIY”
Algorithm :
- Write down the plain text message as a sequence of diagonals.
- Read the plain text written in step1 as a sequence of rows.
20. Explain transposition Cipher?
Simple columnar transposition:
In a columnar transposition, the message is written out in rows of a fixed length, and then we read it as column by column, and then we choose these columns in some scrambled order.
Both the length of the rows and the permutation of the columns are usually defined by a keyword.
For example :
Suppose we use the keyword ZEBRA and the message, WE ARE DISCOVERED FLEE AT ONCE.
In a regular columnar transposition, we write this into the grid as Follows:
Z E B R A S keyword length is 6 columns =6
6 3 2 4 1 5
W E A R E D
I S C O V E
R E D F L E
E A T O N C
E Q K J E U
Providing five nulls (QKJEU) at the end. The ciphertext is then read off as:
Read column wise 1-2-3-4-5-6
EVLNE ACDTK ESEAQ ROFOJ DEECU WIREE
Algorithm :
- Write the plain text message row-by-row in a rectangle of a pre-defined size.
- Read message column-by-column. However it can be any order like 2, 3, etc.
- The message thus obtained is the ciphertext message.
In the irregular case, the columns are not completed by nulls:
6 3 2 4 1 5
W E A R E D
I S C O V E
R E D F L E
E A T O N C
E
The cipher text becomes:
EVLNA CDTES EAROF ODEEC WIREE
If the user wants to decipher it, the user has to find out column lengths by dividing the message length by the key length.
Double transposition
By guessing possible column, Single coulumer cipher can be attacked very easily.
In double transposition cipher we apply single transposition twice.
We can use two same keys for both transpositions, or two different keys in double transposition.
Now take the result of previous irregular columnar cipher and here perform second encryption with different key “STRIPE” and permutation “564321”
Thus here we applied double transposition cipher.
S T R I P E keyword
5 6 4 2 3 1
E V L N A C
D T E S E A
R O F O D E
E C W I R E
E
As before, this is read off column wise to give the cipher text:
CAEEN SOIAE DRLEF WEDRE EVTOC
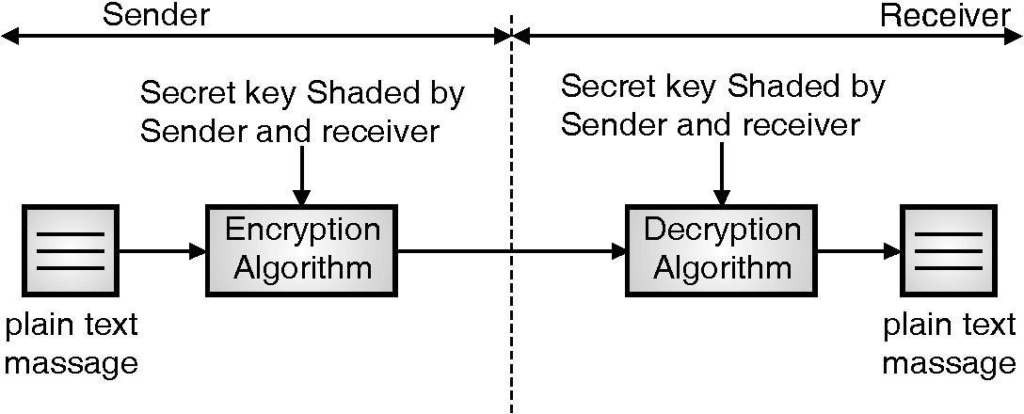
21. Describe Symmetric key encryption?
Symmetric Algorithm:
- In the symmetric algorithm, we use the same key for encryption and decryption.
- Single key or secrete key or shared key algorithm. This key has to kept secret, the sender and receiver use the same key to read encrypted data.
- This key is only the sender and receiver know and no one else.
- The sender and receiver must agree on a key before they communicate. To set up private channels with different parties, you need a new key for each channel. Maintaining a large number of shared secret keys can become a quite tedious task.
Encryption algorithms are divided into two types
- Block Cipher a block cipher encrypts 64-bit blocks of data, with a complex encryption function. Security of these ciphers totally depends on the design of the encryption function. A block cipher encrypts blocks belonging to the same document all under the same key.
- Stream Cipher: It encrypts smaller blocks of plain text data, usually bits or bytes. A stream cipher encrypts the plain text under a continuously changing key stream. Security of these ciphers depends on the design of the key stream generator.
22. Explain asymmetric key encryption?
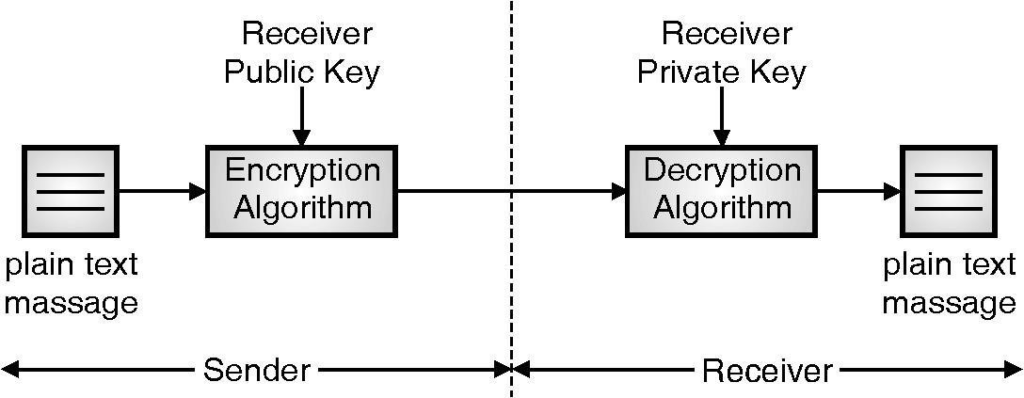
Asymmetric Algorithm:
- Asymmetric Encryption is a form of Encryption where keys come in pairs.
- Frequently the keys are interchangeable, in the sense that if key A encrypts a message, then B can decrypt it, and if key B encrypts a message, then key A can decrypt it. While common, this property is not essential to asymmetric encryption.
- Asymmetric Encryption is also known as Public Key Cryptography, since users typically create a matching key pair, and make one public while keeping the other secret.
- Users can sign messages by encrypting them with their private keys. This is effective since any message recipient can verify that the user’s public key can decrypt the message, and thus prove that the user‟s secret key use to encrypt it.
- If the user’s secret key is, in fact, secret, then it follows that the user, and not some impostor, really sent the message. Users can send secret messages by encrypting a message with the recipient‟s public key. In this case, only the intended recipient can decrypt the message, since only that user should have access to the required secret key.
- The key to the successful use of Asymmetric Encryption is a Key Management system, which implements a Public Key Infrastructure.
- Without this, it is difficult to establish the reliability of public keys or even to conveniently find a suitable one.
23. Difference between block cipher and stream cipher?
| Block Cipher | Stream Cipher |
|---|---|
| This is a type of cipher, which converts plain text into cipher text by blocks a time. | This is a type of cipher, which converts plain text into cipher text bit by bit. |
| No of bits use 64 or more. | No of bits-8. |
24. Difference between Substitution and transposition cipher?
| Substitution Cipher | Transposition Cipher |
|---|---|
| In this cipher, Given plain text letter is replaced by some other letter based on a key value. | In this cipher, Given plain text is arrange into matrix based on key length and then we read encrypted text column wise. |
| Example- caesar’s cipher | Example- rail fence cipher. |
25. Difference between Symmetric and asymmetric key cryptography?
| Symmetric key cryptography | Asymmetric key Cryptography |
|---|---|
| Single key is used for encryption and decryption. | Two separate keys are used for encryption and decryption. |
| The encryption process is very fast. | The encryption process is slow. |
| Example- DES algorithm | Example RSA algorithm |
Click here for more Interview Questions
Latest Posts
- 100+ Core Java Interview Question And Answers
- Top 50 SQL Interview Questions And Answers
- Top 40 Computer Network Interview Questions.
- Top 30+ SQL Queries Questions Asked In Interview
- Top 25 Cybersecurity Interview Questions With Answers.
- Top 35+ | Operating System Interview Questions & Answers
- SQL Queries On Sailors Schema with Solutions
- Selenium Interview Questions | Top 50
- Data Engineer Interview Questions and Answers | Top 50
- 50 Top Networking Interview Questions and Answers
- Design Patterns Interview Questions | Java